A wise man once said, “Water Tribe” as he proudly flicked his wrists in a dramatic exit following his younger sister. This wise man was a young man named Sokka, from the Avatar: the Last Airbender. Now I know what you’re thinking — I promise, I’ll get to the actual exhibition in a second — what do fictional animated characters like Sokka and Katara and the “Water Tribe” have to do with Inuit art?
Before I answer this seemingly pointless question, let’s talk about the Tillirnanngittuq exhibition! First, a quote from the UMMA website:
Tillirnanngittuq, pronounced “tid-ee-nang-ee-took,” means ‘unexpected’ in the Inuktitut language. Mame Jackson, curator for this exhibition explains: “Tillirnanngittuq refers to the astonishing outpouring of Inuit art since the 1950s—a truly amazing story! Neither the Inuit artists nor those who worked with them in the early years could have foreseen the worldwide acclaim Inuit art would achieve.”
The Power Family Program for Inuit Art: Tillirnanngittuq exhibition showcases 58 works of art from the collection of Philip and Kathy Power. Most of these works are from the 1950s and 60s—the earliest years in the development of carvings and prints by the Inuit of the Canadian Arctic. The entire Power Collection of Inuit Art, gifted to UMMA in 2018, includes more than 200 sculptures and prints.
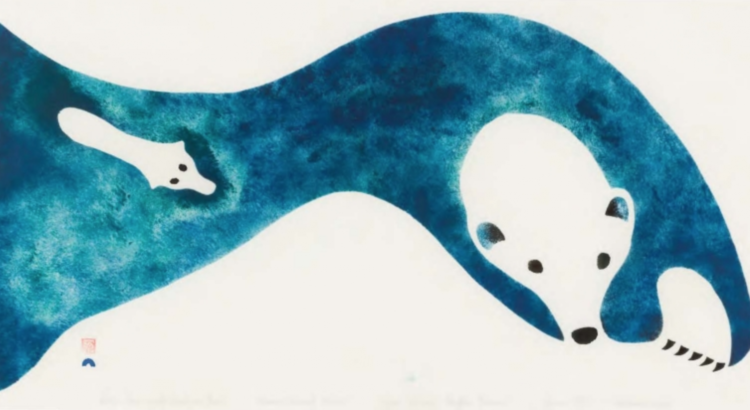
Visitors will discover innovative stonecut and stencil prints, and exquisite stone, bone, and ivory sculptures of arctic animals based on the artists’ life experience as traditional hunters, attentive in their observation and understanding of the animals in their environment. Slightly abstracted, this art possesses great character and vitality, elegance of line and form. The artists illustrate not only reality from nature such as how polar animals move, but also inventive design choices as they multiply, overlap, and interweave natural forms.
I felt very honored and privileged to witness the beauty of Inuit art, learning about their cultural history through their carved ivory and stone, their etched drawings, and their deceptively “simple” prints. The guided tour and mini history lessons provided commentary and contextualized each piece, talking about the Inuit peoples’ works of art catering to a more globalized economy.
Among the intriguing Inuit things I’ve learned at the gallery, I learned their value of family, some of their past day-to-day practices and customs, such as the importance of sharing stories with one another and their deep connection with nature, coexisting and living together in harmony, and I learned that in times of industrialization, the Inuit have had to switch business practices, as their usual nomadic lifestyle and hunting methods were no longer sustainable in the fast-paced, industrialized world. According to the art historian and curator, one of the things the Inuit turned to as a solution, was their art.
Now, back to my original question: what do fictional animated characters like Sokka and Katara and the “Water Tribe” have to do with Inuit art?
For me, they have everything to do with it.
As a child, I was completely unaware of indigenous peoples and their cultures, with the exception of some minor obligatory history lessons in high school. I’ll admit, I was probably a bit luckier than others in my younger days, because my Michigan elementary school field trips often considered Native American history and culture, where my classmates and I were each given tiny stone arrowheads and cute little pamphlets to take home and share with our families. It was never anything I took seriously, I took everything for granted in my childhood. But then, I started watching Avatar: the Last Airbender.
Now, forgive me for fangirl-ing, but this kids’ animated TV show continues to exist as an absolutely incredible, sophisticated, enlightening, and alarmingly impactful story to me! I’ll spare you the excruciating details, but it handles the multifaceted ideas of ethnicity and indigenous peoples, in tandem with the benefits and drawbacks of colonization and industrialization, discussing crucial topics related to the environment, spirituality, morality, and pacifism in times of war and hardship. It’s definitely a timeless classic for my generation, and for little kid me, it was a pretty big game-changer, without me even realizing it.
Now, as a (somewhat) full-fledged adult, I’m aggressively cognizant of anything to do with marginalized ethnic groups, the “colonizers” and the “colonized,” and basically anything to do with that often rocky relationship. It’s important to understand that these people exist, and representation in this day and age is unbelievably crucial to raise awareness and bring our attention to their history and culture.
Avatar: the Last Airbender might have used the world of fiction to send positive and powerful messages, but the creators themselves admitted to drawing inspiration from the Inuit for the Water Tribe people. As a child, being exposed to people who looked Inuit, even if they were calling themselves “Water Tribe” in the show, ultimately had a lasting effect on me. To be completely honest, I was excited to see the Tillirnanngittuq exhibition partly because of my fondness for the “Water Tribe.” That somehow, what I saw in the exhibition was related to my childhood fascination with the Avatar world and the four nations, particularly the “Water Tribe” and their arctic homes. And I think this just goes to show, the younger and more impressionable audiences, need to be exposed to different cultures and people. It’s extremely important, not only for the sake of diversity but for everyone to understand that the world doesn’t revolve around a singular group of people.
My history classes, K-12 and now at U-M, has taught me that the way history is shaped, the “world” really feels American and Euro-centric. I massively appreciate the Tillirnanngittuq exhibition at the UMMA because it is an opportunity not just to appreciate Inuit art, but ultimately to learn about Inuit history and culture in a society that has long disregarded and erased the cultural histories of these indigenous peoples.
Did I use this post as an excuse to fangirl about Avatar: the Last Airbender? Maybe. Did I use this post to rant about post-colonialism and the importance of racial/ethnic diversity representation in media? I sure hope so. Did I learn anything about the actual Inuit people in writing about the Tillirnanngittuq exhibition itself? Definitely. And am I about to tell you to go see the Tillirnanngittuq exhibition while it’s still at the UMMA? Absolutely.
The Tillirnanngittuq exhibition will be there until October 6, 2019. I hope that everyone will make the effort to go see the beautiful and inspiring Inuit art and learn about their history and culture. I hope that instead of focusing on traditional European paintings and Asian Buddhist statues, everyone will take a look at Inuit ivory and stone carvings, etchings, and prints and walk away knowing that there are so many marginalized groups out there that deserve recognition, representation, and most importantly, respect.